3. PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY
MICROPROPAGATION
Objective of Project
Research Approach / Methodology
Expected Results
Significance of Project and Commercialization Potantial
ISOLATION OF POD-SPECIFIC PROMOTER
Objective

Biotech Glossary |
Bioinformatics |
Lab Protocol |
Notes |
Malaysia University |
4. OTHERS
ISOLATION OF POD-SPECIFIC PROMOTER
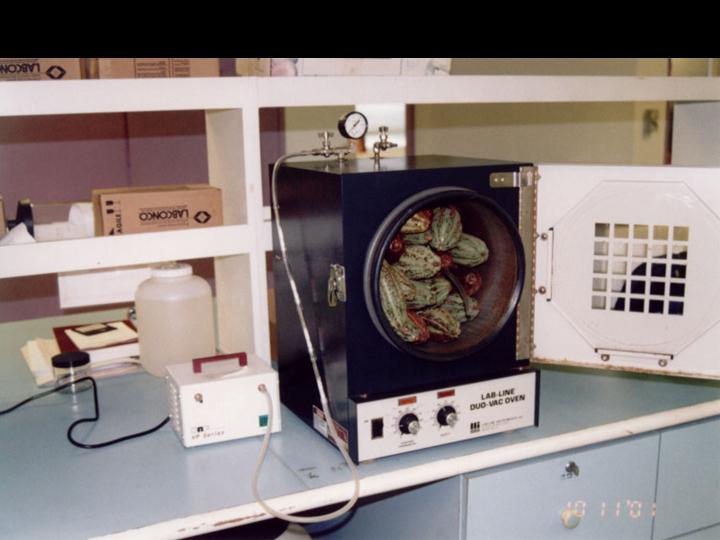
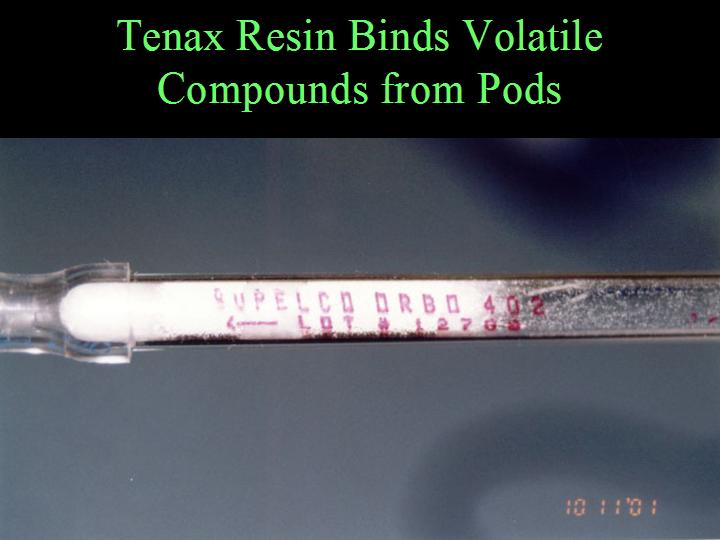
POD KAIROMONES
MICROPROPAGATION
Project Title
Pest resistant cocoa via in vitro technology
Flower explants are placed on nutrient media containing phytohormones to induce cell proliferation. Resultant calli are then transferred to similar media lacking phytohormones. After several weeks somatic embryos may appear. These primary somatic embryos can then be processed like the initial flower explants in order to induce secondary somatic embryos or placed on special media to induce plantlet development.
We have regenerated dozens of plants from several clones, but the frequencies of primary and secondary somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration are still too low to mass propagate trees and to create transgenic trees.
Our bean buyers will have no objection to beans from micropropagated trees because no genetic modification technology is involved.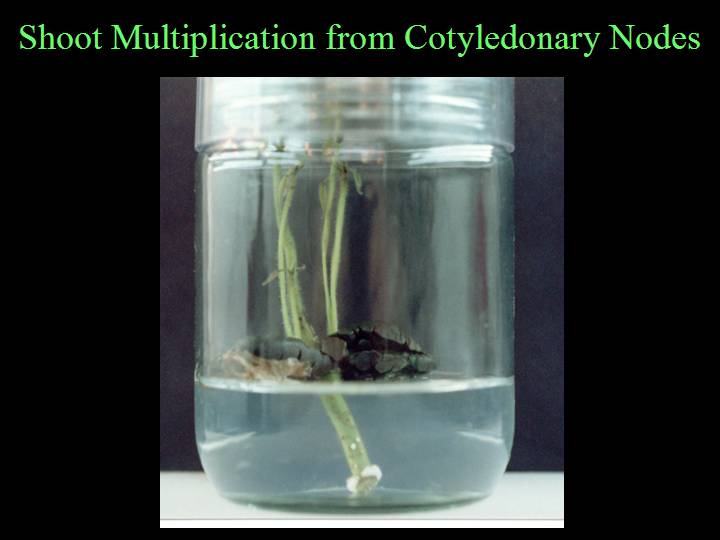

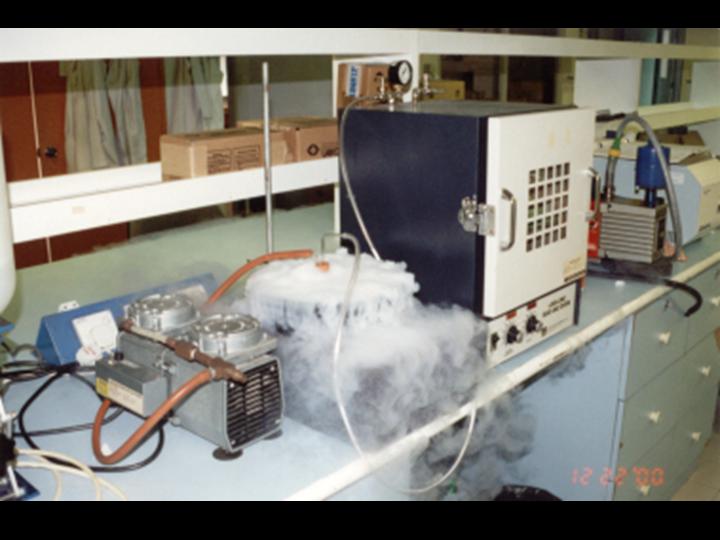
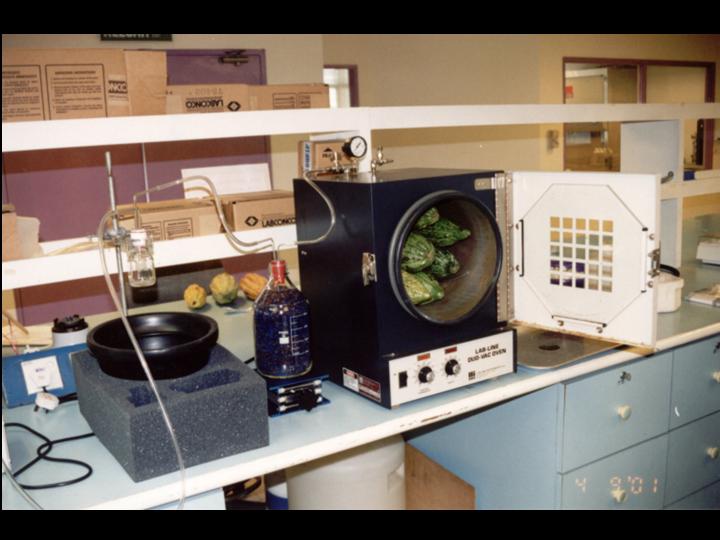
POD KAIROMONES
Objective